How We Collect Them:
You may need to have more than one colonoscopy or biopsy during the clinical trial. The research center staff will tell you how to prepare for the colonoscopy. Follow the preparation steps carefully in the days before your scheduled procedure.
Colonoscopy preparation tips:
-
Preparation is key
- Good preparation for the colonoscopy procedure is critical to the success of the trial and avoid repeating the colonoscopy.
- Discuss your preparation procedure with the research center staff. You may be able to make adjustments to the preparation medications, depending on your specific needs. Let the research center staff know if you are having trouble or difficulty during the prep.
Know your body
Stay organized
Have support
Other tips
Are Food Triggers The Only Cause Of An Ulcerative Colitis Flare
Regardless of your diet, there may be times when your ulcerative colitis symptoms seem to disappear completely for months at a time before making a dramatic reappearance. When this happens, its .
But the foods youre eating arent the only possible culprit. Emotional stress, not taking medications as prescribed, and use of certain medications, like steroids and antibiotics, can also trigger ulcerative colitis flares, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Flares take different forms for different people, and theres no formula that predicts what will bring them on. Different people will claim a medicine or anxiety will set their symptoms off. But some people just seem to have had flares when they have flares, and you can drive yourself crazy trying to find the cause, Dr. Schwimmer says.
When Should Someone Contact A Doctor About Colitis
Diarrhea is a common sign of colitis. It is usually self-limited and resolves on its own with supportive care, including rest and a short course of a clear-fluid diet. However, seek medical care if diarrhea persists for more than two to three weeks, if there is blood in the stool, fever, or the person has signs of dehydration.
- Blood in the stool is never normal and should always be evaluated. Common causes of blood in the stool include hemorrhoids however, other serious causes of bleeding need to be investigated. Colitis is not the only cause of rectal bleeding. Other causes include diverticular disease of the colon , colon polyps, anal fissures, and cancer.
- Chronic diarrhea may lead to dehydration and changes in the electrolyte balance in the body. If it is severe enough, the dehydration may require treatment with IV fluids or oral rehydration therapy. The symptoms of dehydration may include
- lightheadedness , especially when changing from a sitting or lying position to a standing position
- weakness
You May Like: Snack Ideas For Ulcerative Colitis
Overview Of Ulcerative Colitis
While it can be overwhelming to receive a chronic disease diagnosis, learning all you can about ulcerative colitis will prepare you to manage your symptoms and live a full life.
Have you or a loved one been recently diagnosed with ulcerative colitis? Or were you diagnosed years ago but still dont fully understand your disease? Check out our latest video chat to learn more.
Video Length00:38:13
Video Chat: Ulcerative Colitis 101
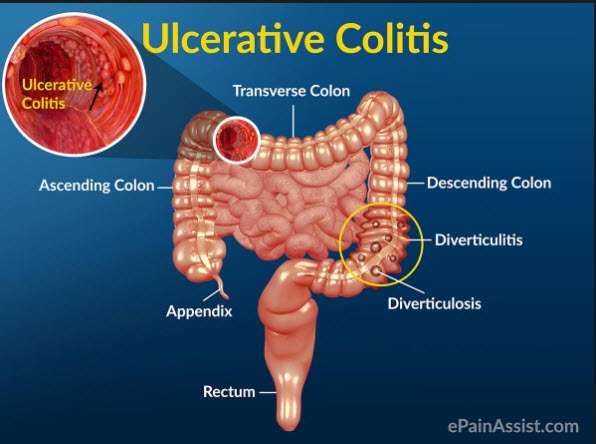
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the large intestine, also called the colon, that affects the lining of the colon and causes small sores, or ulcers, to form.
Those ulcers produce pus and mucous, which cause abdominal pain and the need to frequently empty your colon.
Video Length00:06:55
Ulcerative Colitis 101 This introductory video provides information on potential causes, symptoms, treatment and overall management of ulcerative colitis.
What Is A Flare
When you have ulcerative colitis, your physician will try to find the right medications to control your symptoms. However, since there is no cure, the systemic disease is always there. When the symptoms arent present, you are in remission. If the symptoms return, especially if they are worse than before, it is a flare. This is why it is important to continue taking any medications your doctor prescribes, even if you feel better. If you stop taking your medication, then you can increase your chance of experiencing a flare and progression of the disease. Infections, stress, and taking antibiotics or NSAIDs can also make you more susceptible to a flare.
Also Check: Can I Eat Oatmeal With Ulcerative Colitis
Does A Colectomy Cure Ulcerative Colitis
- One possible treatment for ulcerative colitis is a colectomy, in which all or part of the colon is removed.
- A colectomy will likely help relieve all colon-related symptoms.
- After a colectomy, people with UC may still have other health problems related to other organs, or they may experience lifestyle changes caused by the surgery.
Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease in which the immune system attacks the large intestine . UC causes inflammation and ulcers to form. If the large intestine becomes too damaged or causes severe health problems, your doctor may remove all or part of the colon and rectum in a procedure known as a colectomy, colon resection, or large bowel resection.
There are several types of colectomy procedures. For most people with UC, removing the full large intestine can resolve the majority of their symptoms. Moreover, most people who have a colectomy are able to resume their regular activities and hobbies. Still, undergoing the procedure may also require some lifestyle changes, which can take some getting used to. Understanding the options available and their potential impacts will help you engage in an informed conversation with your health care provider.
Signs Of Possible Colitis
General signs of colitis can include:
- Intense pain
- Swelling of the colon tissue
- Erythema of the surface of the colon
- Ulcers on the colon which may bleed
- Mucus and/or blood in stool and rectal bleeding
- Diarrhea, which may occur, although some forms of colitis involve constipation so the stool and bowel movements may appear normal.
Other symptoms may include gas, bloating, indigestion, heartburn, gastro esophageal reflux disease, cramps, bowel urgency and many other uncomfortable aches in the gastrointestinal system.
Also Check: Ulcers In Small Bowel Crohn’s
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With Colitis
Patients with infectious diarrhea tend to get better relatively quickly with supportive care. Most infections will resolve with or without specific treatment and often do not require antibiotics. Those decisions depend on the patient’s diagnosis.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease probably will require lifelong treatment to help control their symptoms. The goal, as with any long-term illness, is to allow the patient to live a normal life with minimal symptoms from the disease.
Patients with ischemic colitis need to minimize their risk factors for progressive narrowing of the arteries. These are the same risks as for heart disease and require the same treatment approach, including controlling high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and smoking cessation. Patients with severe ischemia that leads to a dead colon require surgery to remove the gangrenous segment.
Vitamin And Mineral Supplements For Ibd
A person with IBD who eats a healthy, varied diet does not usually need to take vitamin supplements. But if they have a dietary deficiency, they may need tablets or occasional vitamin B12 injections. For example, a person on a low-fibre diet may need extra vitamin C and folic acid because they dont eat enough fruit and vegetables.A person with Crohns disease who experiences steatorrhoea may need calcium and magnesium supplements. Most children with IBD should take supplements to help them grow and develop normally.
Read Also: Different Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
Effects Of Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Every person responds differently to IBD. The severity of symptoms will vary from time to time and from person to person. IBD is not a progressive disease . Rather, flare-ups can range from mild to severe and back to mild again. Some people will experience periods of relief from symptoms in between flare-ups.We cannot predict how long a person will stay free from symptoms, or when their next flare-up will occur. Some flare-ups settle down quite quickly with treatment. Other times, it may take months for a persons symptoms to respond to treatment.IBD interferes with a persons normal body functions. Signs and symptoms can include:
- pain in the abdomen
- delayed or impaired growth in children.
Living With Ulcerative Colitis
With careful management, most people with UC are able to enjoy life, including work, travel, recreation, sex and having children.
To keep healthy, consider:
- eating a nutritious diet to help with healing and reduce fatigue
- keeping a food diary to check if there are any foods that make your symptoms worse during a flare-up
- asking your doctor about supplements if you think you may be malnourished
- exercising regularly to lift your mood and help relieve stress
- learning some relaxation techniques to help manage stress
Also Check: How Long Does An Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last
The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is also an inflammatory bowel disease . The 2 diseases affect the digestive tract differently:
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the large bowel , and inflammation is only in the surface layers of the bowel lining. It causes ulcers to form in the lining of the bowel.
- Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus , but usually just the last section of the small bowel and/or the colon. Inflammation can extend into the entire thickness of the bowel wall.
Actions For This Page
- Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease .
- Crohns disease can appear in any part of a persons digestive tract from mouth to anus.
- Ulcerative colitis is located only in a persons large bowel .
- Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD.
- Medications help manage the symptoms of IBD.
- People with IBD can lead useful and productive lives.
- Some dietary changes can help you manage symptoms of IBD and allow medications to work better.
- Always talk with your doctor, healthcare specialist or dietitian before changing your diet. Arrange an emergency plan of action with your doctor, including after-hours phone numbers.
Recommended Reading: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Blood In Urine
Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Colitis
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two types of inflammatory bowel disease that cause colitis. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are considered autoimmune diseases .
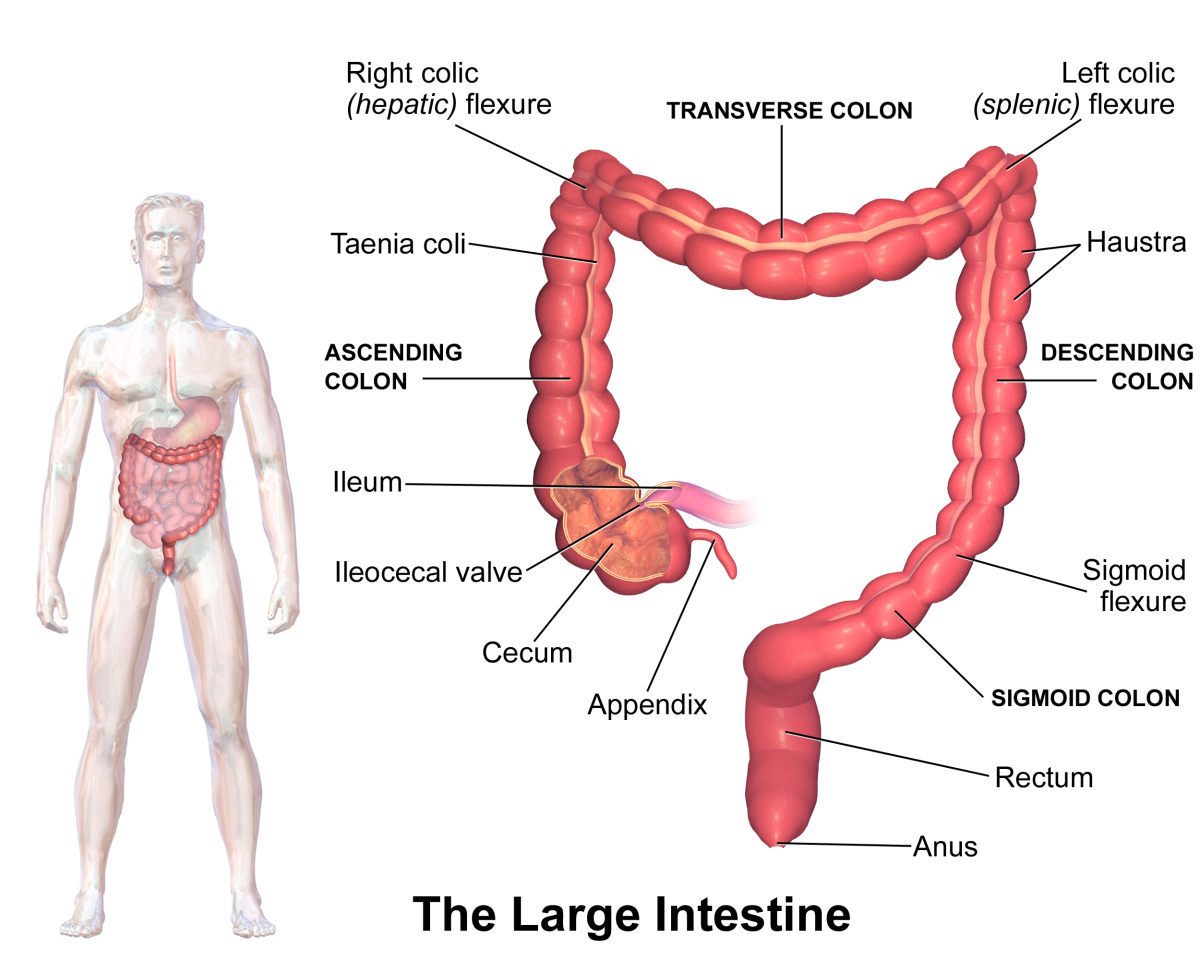
- Ulcerative colitis always begins in the rectum and may spread to the rest of the rest of the colon, spreading from the rectum to the sigmoid, descending, transverse, and finally the ascending colon and cecum in that order. Ulcerative colitis is considered an autoimmune disease, and symptoms include abdominal pain, and bloody, diarrheal bowel movements.
- Crohn’s disease may occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract , including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. In Crohn’s disease, there may be “skip lesions,” that is, abnormal segments of the GI tract interspersed with normal segments.
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may have other organ systems involved in addition to the gastrointestinal tract.
Either collagen or lymphocytes infiltrate into the layers of the wall of the colon, presumably as a result of inflammation. This is an uncommon illness and maybe an autoimmune disease. Diarrhea often is watery, and no blood is present in the stool.
Ulcerative Colitis Care At Seattle Childrens
Seattle Childrens has a special IBD Center to care for children with this complex condition.
- The experts you need are here
The clinic provides access to many IBD experts. We can schedule your visit so your child sees many of them in one place on the same day. We treat your whole child by combining care from specialists in digestive health, immune health, nutrition, surgery and psychology.
- We offer advanced treatments, including nutrition therapy
Through our IBD Center, we offer advanced treatments for children with ulcerative colitis that are not offered everywhere. This includes nutrition therapies such as the Specific Carbohydrate Diet . Our surgeons have the most experience in the region doing the highly technical surgeries that some children with ulcerative colitis need.
Read about our clinical trials using SCD to treat ulcerative colitis and other forms of IBD.
- Early therapeutic medicine monitoring
- One of the early signs of remission is how much medicine is still in your childs body after a certain amount of time. We will check your childs medicine levels early so we can individualize the dose, and increase the likelihood of your child getting and staying in remission.
Read Also: Can You Drink Coffee With Ulcerative Colitis
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis
Anyone at any age, including young children, can get ulcerative colitis. Your chance of getting it is slightly higher if you:
- Have a close relative with inflammatory bowel disease .
- Are between 15 and 30 years old, or older than 60.
- Are Jewish.
- Use frequent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen .
Ulcerative Colitis In Children
According to one study of IBD in the United States, 1 in 1,299 children between ages 2 and 17 years old were affected by the condition in 2016. Crohns disease was twice as common as UC, and boys were more likely to have IBD than girls.
For children with IBD, a diagnosis is more likely after 10 years old.
UC symptoms in children are similar to symptoms in older individuals. Children may experience bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and fatigue.
In addition, they may experience issues compounded by the condition, such as:
- anemia due to blood loss
- malnutrition from poor eating
- unexplained weight loss
UC can have a significant effect on a childs life, especially if the condition isnt treated and managed properly. Treatments for children are more limited because of possible complications. For example, medicated enemas are rarely used as a treatment method in children.
However, children with UC may be prescribed medications that reduce inflammation and prevent immune system attacks on the colon. For some children, surgery may be necessary to manage symptoms.
If your child has been diagnosed with UC, its important that you work closely with their doctor to find treatments and lifestyle changes that can help. Check out these tips for parents and children dealing with UC.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Ulcer In Female
Ibd And Changing Your Diet
Some dietary changes that may help a person with IBD include:
- Low-fibre diet when IBD is active, most people find a bland , low-fibre diet helps to ease diarrhoea and abdominal cramping. People with Crohns disease who have a narrowed small intestine may need to eat a low-fibre diet most of the time.
- Low-fat diet people with Crohns disease who experience steatorrhoea may benefit from a low-fat diet.
- Low-lactose diet the milk sugar lactose is broken down by the enzyme lactase, commonly found in the lining of the small intestine. Some people with Crohns disease lack this enzyme, so should avoid milk and other dairy products. Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed with a simple test ask your doctor.
- Liquid diet a person with severe Crohns disease may need a nutritionally balanced liquid diet.
- Plenty of water people with IBD need to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis Flares
Ulcerative colitis flares can be caused by a variety of things, including:
- Skipping medications or not taking the correct dose. If you regularly take medicine for your ulcerative colitis, you need to be consistent even when your disease is in remission. If you dont follow prescription instructions, flares can occur.
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Common drugs like aspirin, naproxen, and ibuprofen can inflame the bowel and bring on serious symptoms. If you need mild pain relief or fever treatment, you should take acetaminophen.
- Taking antibiotics. Although theyre useful when you have bacterial infections, they affect the bacteria that live in your intestine. These changes can result in diarrhea or the growth of too much of a certain bacteria that then causes inflammation. If you have a bacterial infection, make sure your healthcare provider knows you have ulcerative colitis.
- Not managing stress. Physical and emotional stress can bring on flare-ups. Once you understand that stress causes such a reaction, you can find out what stress management strategies work to keep flare-ups at bay.
- Eating and drinking triggering items. The foods and drinks that bring on symptoms vary by person. Youll need to track your diet so you can pinpoint triggering items when you experience ulcerative colitis flares.
You May Like: How To Prevent Pressure Ulcers In Wheelchairs
What Happens During Ulcerative Colitis
The cause of ulcerative colitis, which is called pathophysiology, is not well understood. It’s thought that it may be connected to something causing the bacteria and other microbes that normally live in the colon to be out of balance, leading to an immune response and inflammation.
However, there is research underway that has started to uncover some of the reasons why people might develop the disease, including the following.